A Redundant Array of Independent Disks is one of the most efficient and advantageous ways to securely store your data and get instant access to it when required.
Depending on its construction, RAID has several features that enhance the overall safety of stored data and offers high data storage capacity, which can be effectively used. The technology of combining multiple disks into a logical volume – RAID has a huge number of variations.
Practical implementation in storage systems and server equipment can be found in the following specifications: RAID 0, 1, 3, 4, 5, 6, DP, 10, 50, and 60, but commercial applications generally use only some of them. One of the RAID levels used for a high level of security is RAID 6.
RAID 6 Basics
RAID 6 is an array of independent hard drives with two distributed parity checksum schemes that provide fault tolerance and help the system continue operating after the failure of two disks simultaneously. RAID 6 performs checksum calculations based on the Reed-Solomon code algorithm.
RAID 6 is similar to RAID 5 in many aspects but is also more robust because two disk capacities are dedicated to checksums, and two checksums are calculated using different algorithms. The first one is “exclusive or” XOR, and the second requires an additional hard drive Q, so the technology is called a P+Q parity check.
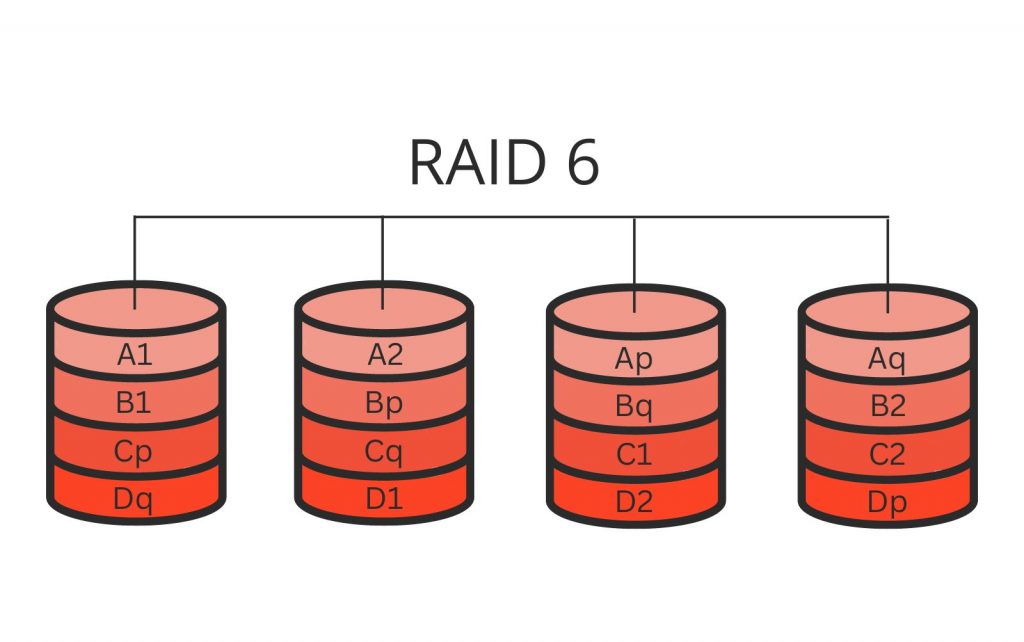
The RAID 6 has a high read speed because the data is stored in blocks and does not have a dedicated disk to store checksums. At the same time, having a large amount of checksum information, the array has a low write speed.
Advantages of RAID 6:
- High level of fault tolerance
- High read speed
- High request processing speed
Disadvantages of RAID 6:
- Low write performance for single small data requests
- Complicated structure and implementation
RAID 6 offers a high level of protection when two hard disk drives fail at once. Still, in many possible application scenarios (e.g., user errors), RAID 6 is not able to provide data availability.
RAID 6 Data Loss
When the redundancy of an array is low, and the file system’s fragmentation level is high, it is possible to have a situation where the failure of one hard drive will make all data on it inaccessible. It is possible to restore the data, but the lack of redundancy sometimes makes it very time-consuming.

Reasons for RAID 6 Failure and Data Loss:
- Controller Failure;
- Accidental Changes in RAID
- Accidental Formatting
- Connection of a Failed Disk
- Failed RAID Rebuild
- Incompatible Disk in the Array;
- Hardware Conflicts
RAID 6 data loss can also occur due to human error, such as accidental deletion or formatting of the array. In some cases, a failed RAID rebuild can also result in data loss.
In addition to these risks, other factors can contribute to RAID 6 failure and data loss. These include controller failure, accidental changes in the RAID configuration, and hardware conflicts.
Our RAID 6 Data Recovery
Recovering data from RAID 6 is a complicated process, and there are various reasons for it. First, at least three drives should crash for the array to fail. Secondly, manufacturers use non-standardized checksum algorithms when implementing RAID 6. Therefore, RAID Recovery Services approaches each case individually, providing customized solutions.
Our data recovery process consists of several critical steps. First, we consult with the client to find out all the details, starting with what happened and ending with what data is most valuable.
Our customer service experts explain the whole process to the client. If there is a need for shipping, we provide instructions, so the device can safely be sent to our facilities.
As soon as we receive your RAID 6 at our lab, our technicians check the performance of the drives and their condition.
If hardware problems are detected, we determine the sequence of solutions.

After finishing our evaluation, we provide a client with a service quote containing all the details about price and timing turnaround. Engineers at RAID Recovery Services work on RAID arrays in specialized facilities using the latest tools. We recover data in an ISO-certified Class 10 Cleanroom, which ensures safe data recovery and maximum results.
Our specialists specialize in RAID devices and restore data using cutting-edge technologies and advanced methods. With years of experience in the field, RAID Recovery Services obtains a 99% success rate and aims to support it with a unique approach to each RAID data loss case.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is RAID 6, and how does it differ from other RAID levels?
RAID 6 is a storage method that uses double parity for fault tolerance. Unlike RAID 5, which has one parity block, RAID 6 uses two parity blocks, enhancing data protection.
What are the considerations when implementing RAID 6 in a storage system?
Setting up RAID 6 normally demands at least four drives, and it’s critical to account for the extra overhead caused by dual parity. It could have a slight impact on both storage capacity and performance.
What are the advantages of using RAID 6 over other RAID configurations?
RAID 6 offers improved fault tolerance compared to RAID 5, particularly in scenarios with a risk of multiple drive failures. The dual-parity system provides better data protection and increased reliability.
How does RAID 6 work in terms of data protection?
RAID 6 distributes data across multiple drives and incorporates dual parity. If two drives fail simultaneously, data reconstruction is possible, providing increased protection against data loss.