In today’s data-driven world, the need for reliable and efficient storage solutions is paramount. When it comes to managing large volumes of data, two commonly used approaches are JBOD (Just a Bunch of Disks) and RAID (Redundant Array of Independent Disks).
Both JBOD and RAID offer distinct advantages and disadvantages, and understanding their differences is crucial for making informed decisions about storage solutions.
In this blog post, we will delve into the characteristics of JBOD and RAID, highlighting their pros and cons to help you choose the right option for your storage needs.
JBOD Basics
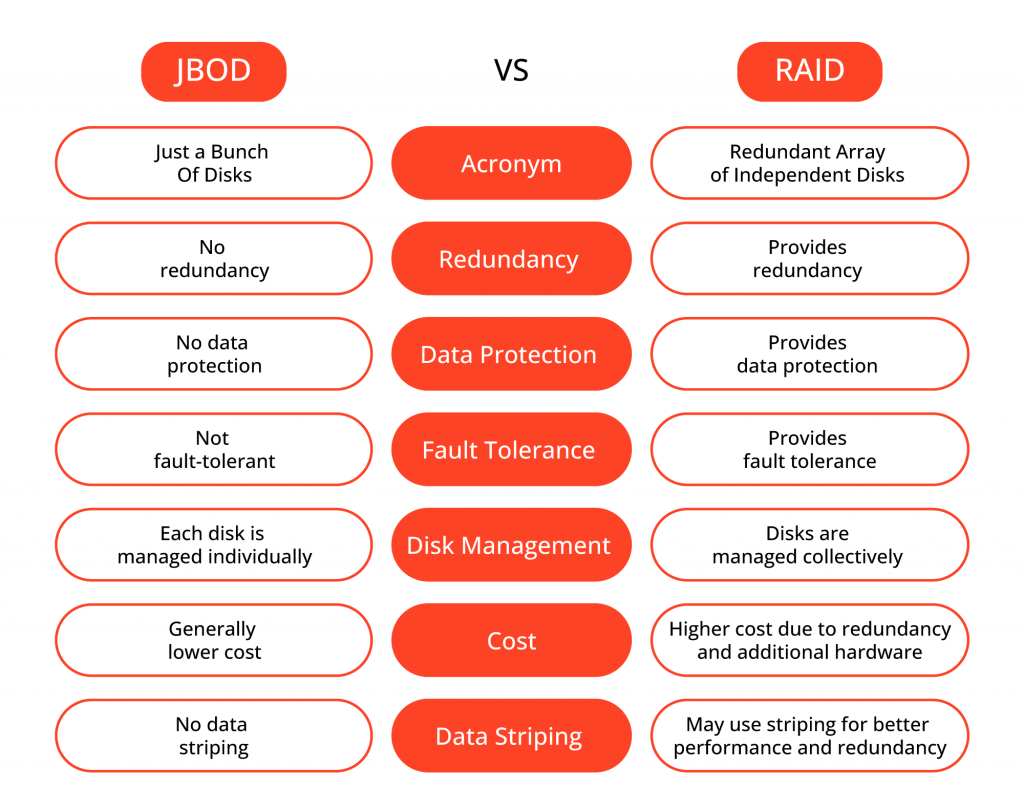
JBOD (Just a Bunch of Disks), as the name suggests, refers to an array of independent disks combined together without any hardware-level redundancy or data striping. In a JBOD configuration, the disks are treated as separate entities, and the operating system sees them as individual drives. Here are some key characteristics of JBOD:
Simplicity
JBOD is incredibly simple to implement since it requires minimal configuration. You can add or remove disks as needed without much hassle.
Maximum Storage Capacity
One of the primary advantages of JBOD is its ability to utilize the full capacity of each individual disk. If you have several large disks and need maximum storage capacity, JBOD can be a cost-effective solution.

No Redundancy
JBOD lacks redundancy, meaning that if a disk fails, the data stored on that disk may be lost. It does not provide any built-in data protection mechanisms.
Limited Performance Benefits
Since JBOD does not offer striping or other performance-enhancing techniques, it may not provide significant performance benefits, especially for tasks involving high I/O loads.
RAID Basics
RAID (Redundant Array of Independent Disks), on the other hand, is a technology that combines multiple physical disks into a single logical unit, offering various levels of data redundancy and performance improvements. Here’s a closer look at RAID:
Data Redundancy
RAID is known for its ability to provide redundancy and fault tolerance. Different RAID levels, such as RAID 1, RAID 5, RAID 6 and RAID 10, offer varying degrees of data redundancy and protection against disk failures
In these configurations, data is distributed across multiple disks, allowing for data reconstruction in case of disk failure.

Improved Performance
RAID configurations, particularly those utilizing striping techniques like RAID 0 or RAID 10, can significantly enhance read and write performance. Striping spreads data across multiple disks, allowing for simultaneous read and write operations, thereby boosting overall system performance.
Configuration Complexity
Unlike JBOD, RAID requires more configuration and management. Setting up RAID arrays typically involves selecting the appropriate RAID level, configuring disk redundancy, and allocating storage space. Additionally, hardware or software RAID controllers may be necessary for optimal performance and management.
Reduced Effective Capacity
While RAID provides redundancy and performance benefits, it comes at the cost of reduced effective storage capacity. Depending on the RAID level and configuration, a portion of the overall disk space is used for redundancy, which decreases the available storage capacity.
Choosing the Right Storage Solution
When deciding between JBOD and RAID, it’s crucial to consider your specific requirements and priorities. Here are a few scenarios where each option may be more suitable:
It is worth noting that there are also hybrid approaches that combine elements of both JBOD and RAID. For example, you can use JBOD to create separate storage pools for specific purposes, while employing RAID for critical data or applications within those pools.
In conclusion, JBOD and RAID offer distinct advantages and trade-offs in terms of simplicity, storage capacity, data redundancy, and performance. By evaluating your specific requirements and understanding the characteristics of each approach, you can make an informed decision on which storage solution best meets your needs. Whether you opt for JBOD or RAID, the key is to strike a balance between cost, reliability, and performance to ensure optimal data management and storage.
Frequently Asked Questions
What does JBOD stand for?
JBOD stands for Just a Bunch of Disks. It refers to a configuration where multiple independent disks are combined together without any hardware-level redundancy or data striping.
What is the main advantage of JBOD?
The primary advantage of JBOD is its simplicity. It is easy to implement and allows you to utilize the full capacity of each individual disk, making it a cost-effective solution for maximum storage capacity.
What is RAID?
RAID stands for Redundant Array of Independent Disks. It is a technology that combines multiple physical disks into a single logical unit, offering various levels of data redundancy and performance improvements.
What is the main advantage of RAID?
The main advantage of RAID is its ability to provide data redundancy and fault tolerance. Different RAID levels offer varying degrees of data protection against disk failures.
Which storage solution should I choose, JBOD or RAID?
Choosing between JBOD and RAID hinges on your needs: JBOD for simplicity and maximum storage; RAID for data protection and performance. Consider cost, reliability, and performance to decide.