Nested RAID Levels are a sophisticated blend of RAID configurations designed to optimize performance, fault tolerance, and storage capacity. They are game-changers in data storage and management but are not immune to failure like any technology. When disaster strikes, it’s imperative to have a reliable partner in data recovery.
This is where RAID Recovery Services comes into play. With a wealth of experience in recovering data from various nested RAID configurations, they have repeatedly shown that no challenge is too big and no detail is too small when restoring your precious data.
In this blog, we will dive deeper into nested RAID levels and how RAID Recovery Services can help you recover your data in case of a malfunction.
Nested RAID Explanation
Nested RAID, or Hybrid RAID, combines two or more standard RAID configurations to create a high-performance, fault-tolerant storage solution. This type of RAID provides the best of both worlds by leveraging the strengths of different RAID levels while minimizing their weaknesses.
One common example of nested RAID is RAID 10 (also known as RAID 1+0), which combines the mirroring of RAID 1 with the striping of RAID 0. This results in improved performance and redundancy, as data is mirrored and striped across multiple drives.
Other examples of nested RAID include RAID 01 (A combination of RAID 0 and RAID 1) and RAID 50 (a combination of RAID 5 and RAID 0).

Each configuration has unique benefits and trade-offs, making nested RAID a versatile option for data storage.
Nested RAID Level Benefits
- Improved Performance: By combining the striping of RAID 0 with the redundancy of other RAID levels, nested RAID can significantly enhance read and write speeds.
- Enhanced Fault Tolerance: With multiple levels of redundancy, nested RAID offers better protection against data loss in case of drive failures.
- Expanded storage capacity: Depending on the type of nested RAID, you can benefit from a larger capacity than traditional RAID configurations. For example, RAID 10 offers a higher storage capacity than RAID 1 alone.
- Flexibility: Nested RAID configurations can be customized to fit specific storage needs, making it an ideal solution for businesses with varying data requirements.
Examples of Nested RAID Levels Include
Before we delve into specific examples nested RAID Levels, it’s important to note that the choice of nested RAID configuration ultimately depends on an organization’s particular needs and priorities. Factors such as performance, resilience to data loss, and storage capacity all come into play. Here, we will share a few examples highlighting the diversity and adaptability of nested RAID levels.
RAID 01 (RAID 0+1)
RAID 01 is a data storage configuration that combines the features of RAID 0 array (striping) and RAID 1 (mirroring) to provide both enhanced storage capacity and data redundancy. RAID 01 involves distributing data across several drives and creating a duplicate copy on another set of drives. This setup guarantees that the data can be accessed from the mirrored drive even if one drive malfunctions. This configuration provides a combination of performance and resilience.
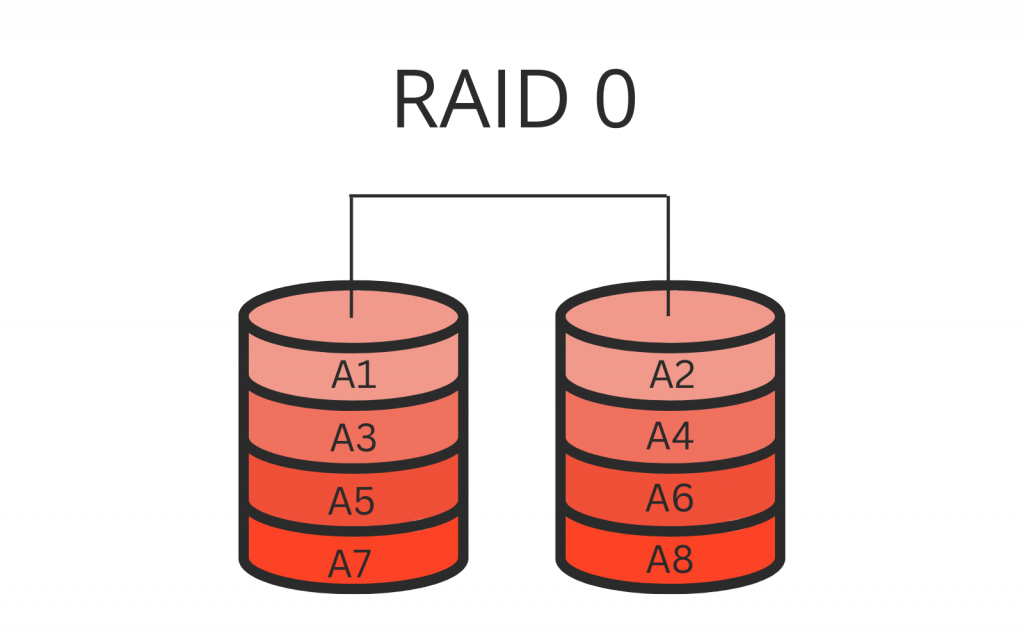
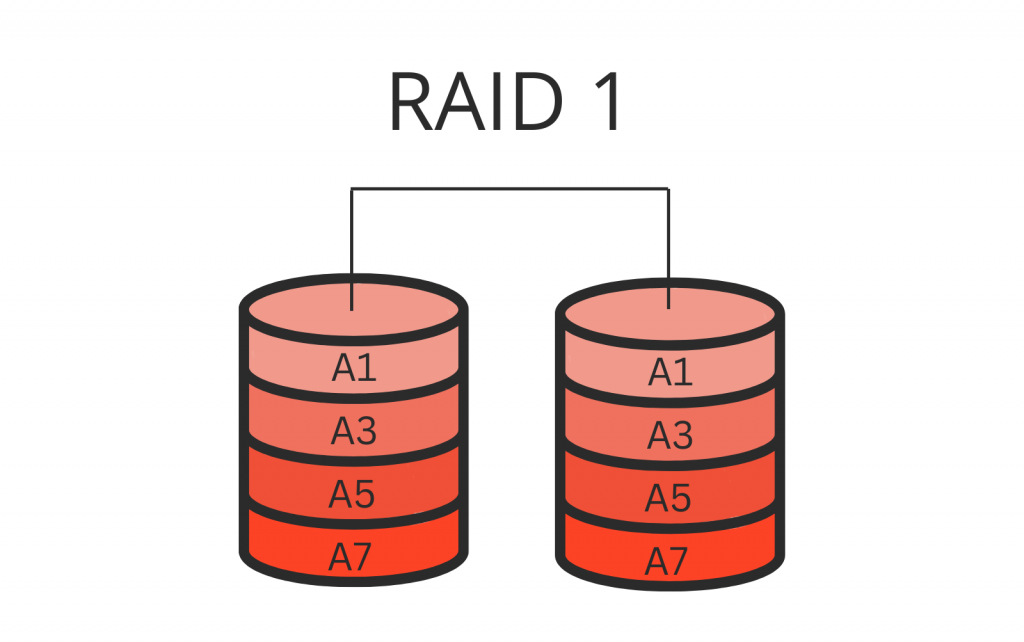
RAID 10 (RAID 1+0)
RAID 10 is a type of nested RAID level that brings together the characteristics of RAID 1 (mirroring) and RAID 0 (striping) to enhance performance and ensure data redundancy. In RAID 10, data is duplicated across multiple drive sets and divided into stripes for faster read and write speeds. This configuration offers both the redundancy of mirroring and the performance benefits of striping, making it well-suited for applications requiring high performance and data protection levels.
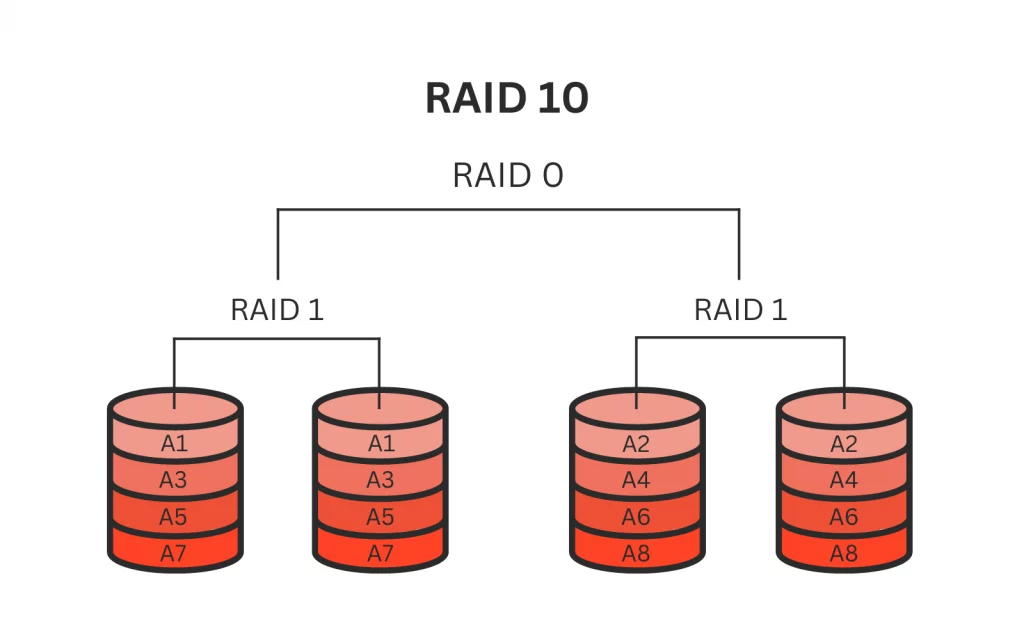
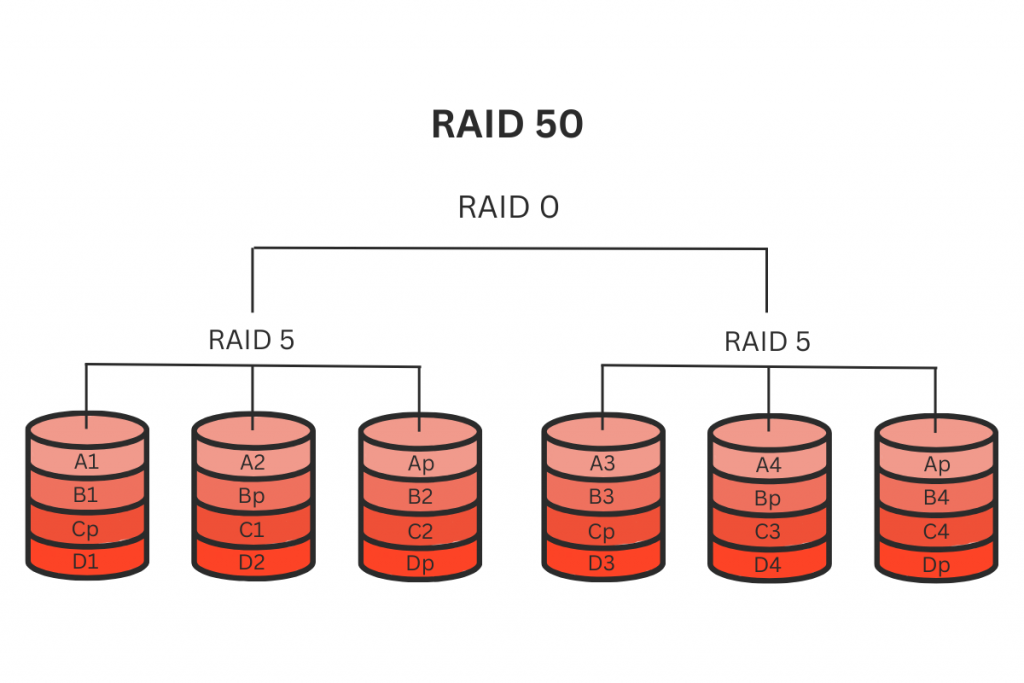
RAID 50 (RAID 5+0)
RAID 50 is a hybrid RAID level that combines the features of RAID 5 (parity-based striping) and RAID 0 (striping) to provide a balance between performance and fault tolerance. In RAID 50, data is striped across multiple sets of drives with parity information for fault tolerance, and then those sets are striped for increased performance. This configuration offers both the benefits of striping for performance and the benefits of parity-based striping for fault tolerance.
RAID 51 (RAID 5+1)
RAID 51 is a hybrid RAID configuration that combines the features of RAID 5 and RAID 1 to provide increased redundancy and performance. In RAID 51, multiple sets of drives are used, where each set is configured in a RAID 5 (parity-based striping) configuration, and then those sets are mirrored using RAID 1 (mirroring). This configuration offers the benefits of both RAID 5 and RAID 1, providing increased redundancy and improved performance.
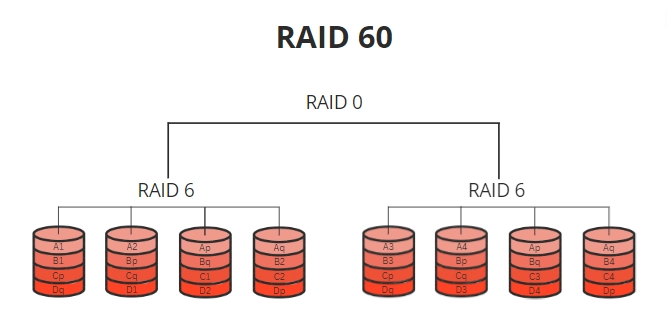
RAID 60 (RAID 6+0)
RAID 60 is a RAID level that combines the features of RAID 6 (dual parity) and RAID 0 (striping) to provide increased performance and fault tolerance. In RAID 60 configuration, data is striped across multiple sets of drives with dual parity for fault tolerance, and then those sets are striped for increased performance. This configuration offers the benefits of both RAID 6 for fault tolerance and RAID 0 for performance, making it appropriate for applications requiring high performance and data protection levels.
RAID 100 (RAID 10+0)
RAID 100 is a RAID level that combines the features of RAID 10 (mirroring and striping) and RAID 0 (striping) to offer high performance and fault tolerance. In RAID 100, multiple sets of drives are used, where each set is configured in a RAID 10 configuration, and then those sets are striped using RAID 0. This configuration provides the benefits of both RAID 10 and RAID 0, offering high performance and data protection levels.


Hybrid RAID Limitations
Hybrid RAID configurations, while offering many benefits such as increased fault tolerance and improved performance, also have limitations. These limitations include the potential for increased complexity in management and configuration and the risk of reduced storage efficiency due to the redundancy inherent in nested RAID setups. When deciding whether to implement a nested RAID configuration in your storage infrastructure, it’s crucial to consider these factors carefully.
- Complexity: Nested RAID can be complicated to set up and manage, requiring high technical expertise.
- Expensive: Due to multiple drives, nested RAID can be more costly than traditional RAID configurations.
- Performance Degradation: In certain nested RAID configurations, performance can degrade significantly if multiple drives fail.
By employing advanced technology and techniques, we can recover your valuable data even in the most complex scenarios. Don’t let the limitations of hybrid RAID stop you from taking advantage of its benefits. Contact RAID Recovery Services today to learn more about our data recovery services.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the difference between standard RAID Levels and nested RAID?
Traditional RAID configurations typically involve using a single level of RAID, such as RAID 0 or RAID 5. On the other hand, Nested RAID combines different levels of RAIDs to offer more advanced features like increased performance and fault tolerance.
Is nested RAID suitable for all types of data storage needs?
No, nested RAID configurations should be carefully considered based on specific organizational needs and priorities. While it offers many benefits, it may not be the best choice for every use case. Consulting with a data storage expert can help determine the most suitable RAID configuration for your needs.
Can nested RAID be implemented in any storage system?
Depending on the specific storage system or hardware, nested RAID configurations may have compatibility limitations. It’s essential to check with the manufacturer for compatibility before implementing a nested RAID setup.
What steps should I take if my nested RAID setup fails?
In case of a nested RAID failure, acting quickly and seeking professional data recovery services is crucial. Attempting to recover the data alone can further damage the drives and make data recovery more challenging. Contact a trusted data recovery partner like PITS Global for expert assistance retrieving your critical data.
Can nested RAID protect against all types of data loss scenarios?
Nested RAID can provide increased fault tolerance but is not a foolproof solution against all types of data loss. It’s important to back up your data regularly and have a reliable data recovery partner in case of unforeseen data loss events.
How can PITS Global help in case of nested RAID failure?
PITS Global has years of experience and expertise in recovering data from all RAID configurations, including nested RAID. Our team of experts utilizes advanced technology and techniques to retrieve your data most efficiently and securely. Contact us today for more information on our nested RAID data recovery services.

