RAID 10 vs RAID 1 is a hot topic for debate among tech enthusiasts and IT professionals looking to optimize storage solutions for business or personal use. This blog post aims to illuminate key differences and similarities between the two configurations. We delve deep into the technical nuances of RAID 10 and RAID 1, discussing their distinct architectures, performance indicators, and data redundancy mechanisms.
What is RAID 10?
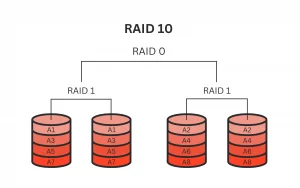
RAID 10, also known as RAID 1+0, is a nested or hybrid RAID setup that combines multiple disks for improved data redundancy and performance. Combines the advantages of both RAID 1 and RAID 0. It requires at least four hard drives and offers excellent performance through striping data across mirrored pairs. In simpler terms, it creates a mirror of two striped sets, providing redundancy for better fault tolerance and improved read/write speeds.
Advantages of RAID 10
- High fault tolerance: With mirroring, the other can continue to function without data loss if one drive fails.
- Improved performance: Data is striped across multiple drives, allowing faster access and transfer rates.
- Easy recovery: In case of a drive failure, rebuilding the array simply involves copying data from the surviving drive to a new one.
Disadvantages of RAID 10
- Cost: RAID 10 requires at least four drives, making it more expensive than other RAID configurations.
- Limited storage capacity: Since half of the drives are used for mirroring, the net usable storage is only half the total capacity.
What is RAID 1?
RAID 1, also known as RAID 0+1, is a non-nested or mirrored RAID configuration that combines the advantages of RAID 0 and RAID 1. It requires at least four drives and offers excellent performance through striping data across mirrored arrays. In simpler terms, it creates stripes of mirrors, providing redundancy for better fault tolerance and improved read/write speeds.
Advantages of RAID 1
- High fault tolerance: With mirroring, the other can continue to function without data loss if one drive fails.
- Improved performance: Data is striped across multiple drives, allowing faster access and transfer rates.
- Easy recovery: In case of a drive failure, rebuilding the array simply involves copying data from the surviving drive to a new one.

Disadvantages of RAID 1
- Cost: RAID 1 requires at least four drives, making it more expensive than other RAID configurations.
- Limited storage capacity: Since half of the drives are used for mirroring, the net usable storage is only half the total capacity.
Difference Between RAID 10 vs RAID 1
The difference between RAID 10 and RAID 1 primarily lies in the way they organize data. RAID 10 uses a “striping then mirroring” approach, which first breaks data into units and distributes them across different drives, then duplicates these striped drives to form a mirrored pair.
In comparison, RAID 01 uses a “mirroring then striping” approach, where it first duplicates data in each drive to form a mirrored pair and then strips these mirrored pairs across different drives. This key distinction impacts their fault tolerance and performance, especially when recovering from a drive failure.
| Features | RAID 10 | RAID 1 |
|---|---|---|
| Minimum No. of Drives | 4 | 4 |
| Data Organization | Striping then Mirroring | Mirroring then Striping |
| Fault Tolerance | High (can survive multiple drive failures as long as they're not part of the same mirrored set) | Moderate (entire stripe fails if one drive fails) |
| Performance | High (data can be read from either mirrored set) | High (all drives can be read simultaneously) |
| Storage Efficiency | 50% (half the drives are used for mirroring) | 50% (half the drives are used for mirroring) |
| Recovery | Faster (only the failed drive needs to be replaced) | Slower (the entire mirrored set needs to be rebuilt) |
RAID 10 vs 1 Fault Tolerance
In RAID 10, if a single drive fails, the mirrored pair can still function, allowing for continued access to data. If two drives fail simultaneously, data can still be accessed if not part of the same mirrored set. However, in RAID 1, if a single drive fails, the entire striped set fails, making it less fault tolerant than RAID 10.
RAID 1 vs 10 Performance
Due to data striping, RAID 10 and RAID 1 offer high read and write speeds. However, RAID 10 has a slight performance edge due to its data storage method. In RAID 10, the controller can read data from either mirrored set, allowing for faster data retrieval in the case of simultaneous read requests.
RAID 10 Recovery and RAID 1 Recovery
RAID 10 offers quicker recovery times than RAID 1 in the event of a drive failure. With RAID 10, only the failed drive needs to be replaced, and the data can be rebuilt from the remaining drive in the mirrored pair. In contrast, RAID 1 requires a complete rebuild of the entire mirrored set, resulting in longer recovery times and a higher risk of data loss if another drive fails during the rebuilding process.
In conclusion, the choice between RAID 10 and RAID 1 depends on your needs. While RAID 10 offers a higher degree of fault tolerance and faster recovery, RAID 1 provides a simpler configuration with similar performance levels.
Unexpected data loss can still occur regardless of the RAID level you choose. RAID Recovery Services are here to help if you are in trouble. With experienced professionals and a proven track record, RAID Recovery Services provides expert RAID recovery and restoration services. Contact us today to learn more about our services.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the main difference between RAID 10 and RAID 1?
RAID 10 uses a “striping then mirroring” approach, while RAID 1 uses a “mirroring then striping” approach in organizing data. This difference impacts their fault tolerance, performance, and recovery times.
Which RAID configuration offers higher fault tolerance?
RAID 10 has a higher fault tolerance. If a single drive fails, the mirrored pair in RAID 10 can still function, and even if two drives fail simultaneously, data can still be accessed as long as they are not from the same mirrored set.
Is there a difference in performance between RAID 10 and RAID 1?
Both RAID levels offer high read and write speeds due to data striping, but RAID 10 has a slight edge in performance. In RAID 10, data can be read from either mirrored set, allowing faster retrieval with simultaneous read requests.
Which RAID levels recover faster from a drive failure?
RAID 10 recovers faster. With RAID 10, only the failed drive needs to be replaced, and the data can be rebuilt from the remaining drive in the mirrored pair, while RAID 1 requires a complete rebuild of the entire mirrored set.
Which RAID level should I choose?
The choice between RAID 10 and RAID 1 depends on your specific needs. RAID 10 offers a higher degree of fault tolerance and faster recovery, while RAID 1 offers a simpler configuration with similar performance levels.
What if I lose data from a RAID setup?
If you experience unexpected data loss from any RAID setup, professional data recovery services like RAID Recovery Services can assist in recovering and restoring your data.