In the realm of data storage and protection, RAID configurations play a pivotal role in maintaining data integrity and availability. Choosing the right RAID level can be a challenging task, with various options available, each offering a unique set of advantages and limitations.
Among these options, RAID 50 and RAID 60 are two commonly utilized configurations. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the nuances, benefits, and drawbacks of RAID 50 and RAID 60 to empower you with the knowledge necessary to make an informed decision.
What is RAID 50?
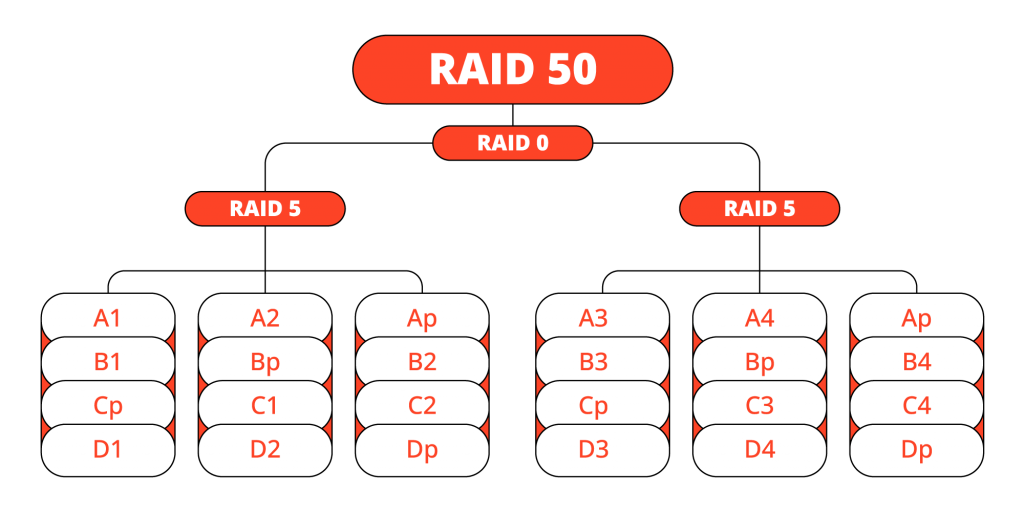
Before diving into a detailed comparison, let’s establish a clear understanding of RAID 50 and RAID 60 by exploring their fundamental characteristics. RAID 50, also known as “striping with distributed parity,” is essentially a fusion of two RAID levels: RAID 5 and RAID 0. Its primary objective is to strike a balance between data redundancy and performance.
In a RAID 50 array, data is striped across multiple RAID 5 arrays, each of which consists of multiple drives.
Parity data is meticulously distributed across these drives to provide redundancy and fault tolerance.
Advantages of RAID 50
- Performance: RAID 50 excels in read and write performance compared to RAID 5 due to data striping across multiple RAID 5 arrays.
- Redundancy: Despite its performance boost, RAID 50 ensures data security through distributed parity, allowing data reconstruction even if a single drive fails within a RAID 5 array.
- Capacity: RAID 50 can accommodate larger storage configurations by combining multiple RAID 5 arrays.
What is RAID 60?
In contrast, RAID 60 is an extension of RAID 6 and RAID 0, designed to enhance fault tolerance and performance while maintaining a balance between redundancy and capacity.
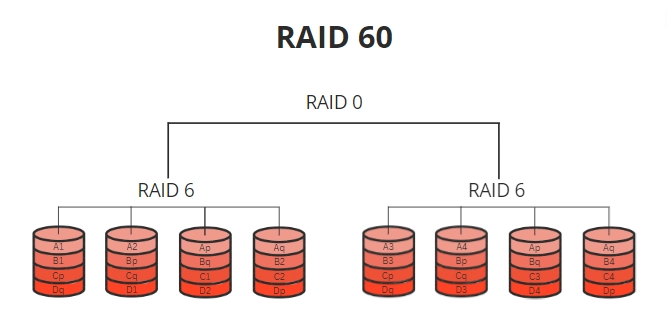
In a RAID 60 array, data is striped across multiple RAID 6 arrays, each of which includes two parity blocks, offering dual redundancy.
Similar to RAID 50, RAID 60 employs striping to enhance performance.
Advantages of RAID 60
- Redundancy: RAID 60 boasts remarkable fault tolerance due to dual parity blocks within each RAID 6 array. It can withstand the failure of up to two drives within a single RAID 6 array without data loss, surpassing RAID 50 in this regard.
- Performance: While not as fast as RAID 50, RAID 60 provides commendable performance, especially for read-intensive tasks.
- Data Integrity: RAID 60 is designed to maintain data integrity even in the face of multiple drive failures, making it suitable for critical applications.
Comparing RAID 50 vs. RAID 60
Now that we have a solid understanding of RAID 50 and RAID 60, let’s conduct a comprehensive comparison across several critical aspects to facilitate your decision-making process.
Fault Tolerance
Both RAID 50 and RAID 60 utilize parity data for fault tolerance. However, RAID 60 offers superior fault tolerance with dual parity blocks in each RAID 6 array. RAID 60 can tolerate the failure of up to two drives in a single RAID 6 array without data loss, whereas RAID 50 can only handle the failure of one drive in a RAID 5 array.
Performance
In terms of performance, RAID 50 generally outpaces RAID 60 across most workloads due to data striping across multiple RAID 5 arrays. However, RAID 60 still offers commendable performance, particularly for tasks requiring intensive data reads.

Capacity
RAID 50 has an advantage in terms of storage capacity because it combines multiple RAID 5 arrays. If maximizing storage space is your primary goal, RAID 50 may be the more suitable choice.
Data Rebuild Time
In case of drive failure, both RAID 50 and RAID 60 require a rebuild process to restore data redundancy. Typically, RAID 50 enjoys a shorter rebuild time due to its involvement with smaller RAID 5 arrays.
On the other hand, RAID 60’s rebuild time can be longer, primarily because of its larger RAID 6 arrays and the computation of dual parity blocks.
Ideal Use Cases
- RAID 50: Well-suited for environments requiring a balance between performance and redundancy, such as file servers, database servers, and virtualization setups.
- RAID 60: Ideal for environments where data integrity and high fault tolerance are critical, such as large-scale enterprise storage systems, online transaction processing (OLTP) databases, and archival systems.
Choosing the Right RAID Level: RAID 60 vs RAID 50
Ultimately, the choice between RAID 50 and RAID 60 depends on your specific requirements and priorities. Here are some key considerations to help you make an informed decision:

- Data Criticality: If data integrity and zero downtime are paramount, RAID 60, with its superior fault tolerance, is the safer choice.
- Performance vs. Redundancy: If performance is a top priority and you have robust backup solutions in place, RAID 50 may be more suitable.
- Budget: RAID 50 tends to be more cost-effective, as it requires fewer drives for the same storage capacity compared to RAID 60.
- Scalability: Consider your future scalability needs. RAID 50 offers more flexible scalability due to its reliance on smaller arrays, while RAID 60 may require adding more drives at once due to its use of larger arrays.
Data Recovery Considerations for RAID 60 vs. RAID 50
While both RAID 50 and RAID 60 offer robust data protection, data recovery can be complex in case of multiple drive failures. At RAID Recovery Services, we specialize in RAID data recovery and have the expertise and equipment to recover data even in challenging scenarios.
In the ongoing debate between RAID 50 and RAID 60, there is no one-size-fits-all solution. Your choice should align with your unique data storage and protection needs. RAID 50 strikes a balance between performance and redundancy, while RAID 60 excels in fault tolerance and data integrity. Regardless of your choice, remember that regular backups and proactive monitoring are essential components of a comprehensive data protection strategy.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the differences between RAID 50 and RAID 60?
RAID 50 offers a balance of speed and redundancy, ideal for medium-sized databases. RAID 60 adds more redundancy, suitable for large capacity servers needing utmost data protection. Choose RAID 50 for performance, RAID 60 for higher fault tolerance.
Which RAID level is more fault-tolerant: RAID 50 or RAID 60?
RAID 60 is more fault-tolerant. It can withstand the failure of up to two drives within a single RAID 6 array without data loss, while RAID 50 can only tolerate the failure of one drive in a RAID 5 array.
When should I choose RAID 50?
RAID 50 is suitable when you need a balance between performance and redundancy. It’s commonly used in environments like file servers, database servers, and virtualization setups.
When should I consider RAID 60?
RAID 60 is an excellent choice when data integrity and high fault tolerance are paramount. It’s often used in large-scale enterprise storage systems, OLTP databases, and archival systems.
What should I prioritize: performance or redundancy?
Your choice should align with your specific needs. If data performance is critical and you have robust backup solutions, RAID 50 might be preferable. For data-critical environments, RAID 60’s superior fault tolerance is a better fit.
Related Blogs

AHCI vs. RAID – Difference Between RAID and AHCI
