A Redundant Array of Independent Disks (RAID) is a term for a storage system that shares and replicates data across multiple hard drives. RAID may be used to provide increased data reliability or increased I/O performance, although one goal may compromise the other.
Level 10 of Redundant Array of Independent Disks represents the system with reversible levels and a stripe of mirrors. The drives in the nested array are combined into RAID 1 mirrors. These mirrored pairs are converted to a single collection using RAID 0 striping.
How does RAID 10 work
RAID 10 enhances data storage by initially establishing two mirrored sets of drives (RAID 1) and then interweaving these sets (RAID 0). This method achieves data duplication and distribution across various drives, offering a combination of redundancy for data protection and a boost in performance.
In the event that one drive in the setup fails, the mirrored set continues to function without any interruption, ensuring that there is no loss of data.
This redundancy is a key feature of RAID 10, offering a layer of data protection not found in simpler RAID configurations.
Additionally, RAID 10 architecture allows data to be written and read across multiple drives simultaneously, enhancing the overall system performance.

This simultaneous operation significantly boosts read and write speeds, making RAID 10 a superior choice in terms of both data reliability and performance compared to other RAID configurations.
RAID 10 Advantages and Disadvantages
RAID 10 offers significant advantages, starting with its superior data protection. By mirroring data, it ensures a high level of redundancy, making it resilient to drive failures. This is critical for businesses where data loss could have grave consequences. Additionally, RAID 10 provides excellent read and write speed, benefiting applications and systems requiring swift data access and processing.
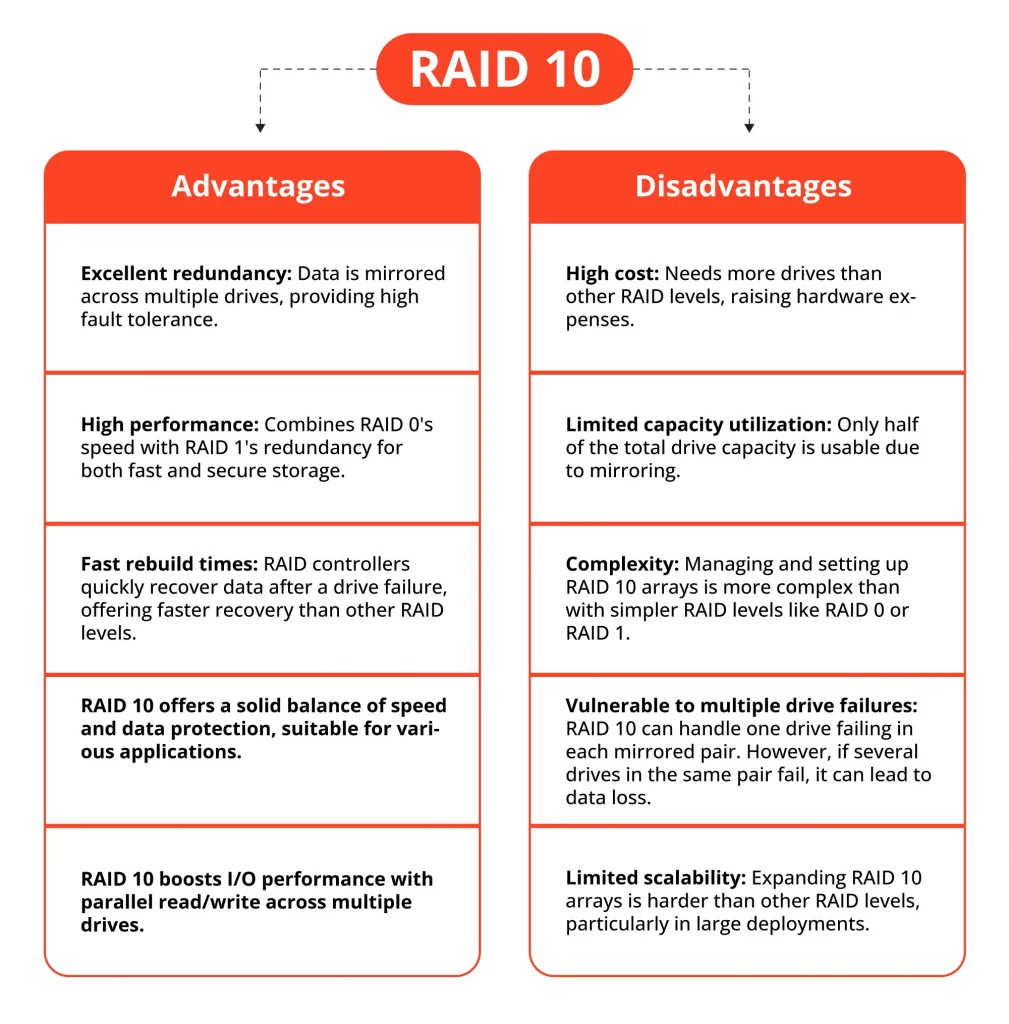
However, RAID 10 has its drawbacks. Its main disadvantage is cost, as it requires double the number of drives for mirroring, effectively halving storage capacity and increasing expenses. Additionally, its setup and maintenance are more complex, demanding technical know-how, which may not suit everyone or smaller setups.
In RAID 10, two drives are striped and mirrored on two other drives, creating a single array. This configuration benefits from high performance (RAID 0) and fault tolerance (RAID 1). RAID 10 provides fast recovery in a drive failure due to data redundancy.
High Performance
The high performance of a RAID is provided by data stripping. The data is divided into blocks in this process, and each block is written or read to a separate disk. Thus, it is possible to perform multiple I/O operations simultaneously. Data stripping is very useful for programs that need high performance and high availability, such software as transactional applications, email, and operating systems.
Fault Tolerance
Mirroring is a traditional way to increase the fault tolerance of a small disk array. In the simplest version, two disks are used, on which the same information is recorded, and in the event of a failure of one of them, its duplicate remains, which continues to work in the same mode. Since each mirroring disk in the array is in working condition, data can be read from them simultaneously.
Comparing RAID 10 to Other RAID Levels
When comparing RAID 10 to other RAID levels, consider the unique balance of performance, redundancy, and storage efficiency each offers. RAID 0, for example, emphasizes performance but offers no redundancy, making it vulnerable to data loss.

RAID 1 provides excellent redundancy by mirroring all data, but it doesn’t enhance performance as RAID 10 does. RAID 5 provides a balance of redundancy and performance by using parity for data protection rather than mirroring.
This approach improves storage efficiency, though it may lead to slower write speeds and extended rebuild times during a drive failure.
RAID 10 combines superior redundancy with high performance, ideal for demanding environments that need both. However, this comes at the cost of storage efficiency and increased expense due to the need for at least four drives. Ultimately, the best RAID level will depend on specific needs and priorities.
Data Recovery Services for RAID 10
RAID has a complicated system, so when a problem with this device occurs, it causes a lot of time and resources for the user. Restoring information from RAID is almost always possible, but only if highly skilled engineers perform this process.
Only a specialized company with advanced tools and years of experience can successfully deal with RAID array failures. RAID Recovery Services offers a wide range of data retrieval solutions to individuals and businesses facing RAID failures.
Our highly trained and qualified engineers can recover any data from mechanically damaged hard drives. They are able to replace the block of magnetic heads, fix spindle motor issues, etc. By professionally emulating RAID operation functions and extracting all the files without any damage, we provide our clients with the highest level of service.
Our data recovery engineers will restore all the priority data in the required timeframe. By using advanced data recovery techniques and cutting-edge technologies, we keep the highest in the industry 99% success rate. Contact RAID Recovery Services at (866) 362-5009 to request professional data retrieval services.
Frequently Asked Questions
How many disks can fail in RAID 10?
In RAID 10, disks are paired to form a mirrored set, so each disk has a duplicate with the same data. Disk failure tolerance in RAID 10 depends on the total disks and their pairing.
What is the minimum hard drive for RAID 10?
RAID 10 requires a minimum of four hard drives, merging the features of RAID 1 and RAID 0. Using more than four disks is advised for higher performance and fault tolerance, increasing the chances of survival against multiple disk failures.
What are the rules for RAID 10?
There are a set of rules that govern how RAID 10 operates and ensures data redundancy. These include:
- Data is mirrored across multiple pairs of disks, with each pair acting as a separate RAID 1 array.
- The number of disks in the array must be an even number.
- If a disk fails, the other operates independently and then rebuilds data from the mirror after replacement.
- If both disks in a pair fail, data loss will occur.
- The usable capacity of a RAID 10 array equals 50% of the combined drives’ total capacity.
Can I turn RAID 1 into RAID 10?
Yes, converting RAID 1 to RAID 10 is possible by adding disks and reconfiguring the array with software or rebuilding it. It’s risky and should be handled by professionals, with all crucial data backed up first.
Which is better, RAID 10 or 01?
The choice between RAID 10 and RAID 01 ultimately depends on the user’s specific needs and priorities. While both configurations offer a similar level of data redundancy, they differ in terms of performance and fault tolerance. RAID 10 offers better read and write speeds compared to RAID 01, as data is simultaneously written to both disks in a mirrored pair.