As businesses of all sizes and individuals increasingly rely on data storage, robust and reliable storage systems become crucial. A Redundant Array of Independent Disks, known as RAID, is one such system that has gained popularity due to its high fault tolerance, performance, and effectiveness.
RAID 50 is a RAID configuration that combines the features of RAID 5 and RAID 0, offering high performance and fault tolerance. In this article, we will explore RAID 50, its advantages and disadvantages, how it works, its capacity, configuration, fault tolerance, minimum drives, and performance.
RAID 50 Understanding
RAID 50 is a nested RAID configuration that uses both RAID 5 and RAID 0. It is also known as RAID 5+0 or RAID 5 with striping. RAID 5 uses block-level striping and parity data across multiple disks to provide fault tolerance, while RAID 0 uses block-level striping to improve performance. RAID 50 combines these two configurations to provide the best of both worlds.
RAID 50 Configuration
RAID 50 array requires a minimum of six drives and two RAID 5. The configuration involves creating two or more RAID 5 arrays and then striping data across them using RAID 0.
The RAID 5 arrays can be created using software or hardware RAID controllers. The RAID 0 array can only be created using a hardware RAID controller. It is important to use high-quality RAID controllers to ensure optimal performance and fault tolerance.

RAID 50 Capacity
The capacity of RAID 50 depends on the number and disk space of the drives used. RAID 50 uses six drives divided into two or more RAID 5 arrays. The capacity of each RAID 5 is the size of the smallest disk drive multiplied by the number of disks minus one. For example, if you have six 1TB drives, the capacity of each RAID 5 array would be 5TB.
The capacity of the RAID 0 array is the sum of the capacities of the RAID 5 arrays. For example, if you have two RAID 5 with a total of 5TB each, the power of the RAID 0 array would be 10TB. Nevertheless, it is essential to note that the smallest drive in the array limits the usable capacity of RAID 50.

RAID 50 Fault Tolerance
RAID 50 provides high fault tolerance using two or more RAID 5 arrays. Each RAID 5 array can sustain the loss of one drive without losing data.
This means that RAID 50 can sustain the loss of up to two drives in the same RAID 5 array without losing data. However, if more than two drives fail simultaneously, data loss is inevitable.
When a drive fails, the system uses the parity data in the RAID 5 array to reconstruct the lost data. This process is known as rebuilding. The rebuilding process can take several hours or even days, based on the array’s size and the drive’s speed.
It is important to note that rebuilding can strain the remaining drives in the array, increasing the risk of another drive failure. Replacing failed drives as soon as possible is recommended to minimise the data loss risk.
RAID 50 Minimum Drives
RAID 50 configuration requires a minimum of six drives. The drives are divided into two or more RAID 5 arrays, with a minimum of three drives per array. The minimum number of disk drives needed for RAID 50 is higher than other RAID configurations, such as RAID 1 or RAID 10, which require a minimum of two and four drives, respectively.
RAID 50 Performance
RAID 50 can provide high performance using RAID 0 striping across the RAID 5 arrays. The RAID 0 striping allows the system to access multiple disks simultaneously, improving read and write speeds. The performance of RAID 50 depends on the number and speed of the drives used.
RAID 50 can provide better performance than RAID 5 or RAID 6, but it is not as fast as RAID 0 or RAID 10. RAID 50 is suitable for applications requiring high performance and fault tolerance, such as database servers, virtualization environments, and media streaming services.
How Does RAID 50 Work?
RAID 50 works by using two or more RAID 5 arrays and striping data across them using RAID 0. The RAID 5 arrays use block-level striping and parity data to provide fault tolerance. The parity data is spread across all the disks in the array, allowing the system to reconstruct lost data in case of a disk failure.
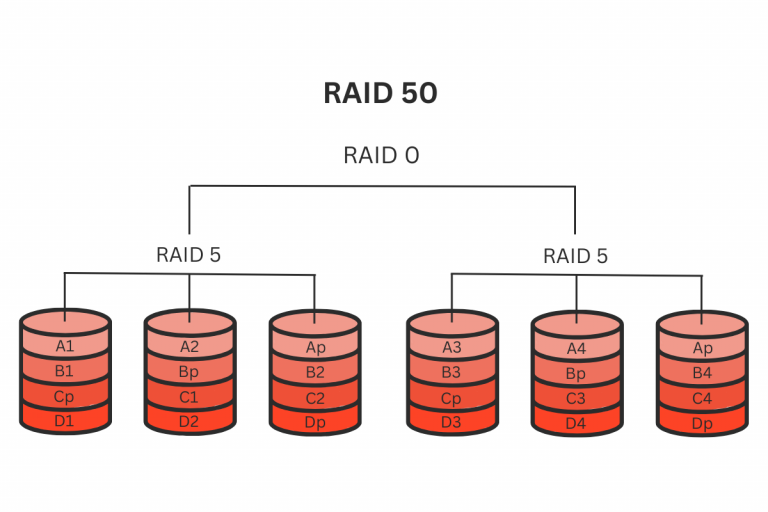
The RAID 0 striping improves performance by spreading data across multiple disks, allowing the system to read and write data faster. The data is divided into blocks and distributed across the disks in the RAID 0 array. This allows the system to access multiple disks simultaneously, improving performance.
RAID 50 Advantages and Disadvantages
One of the main advantages of RAID 50 is its high fault tolerance. It can sustain the loss of up to two drives in the same RAID 5 array without losing data. This makes it suitable for applications that require high availability and reliability, such as database servers, virtualization environments, and media streaming services.
Another advantage of RAID 50 is its high performance. Stripping data across multiple disks can improve read and write speeds. This makes it the best option for applications that require high throughput, such as video editing and rendering.
However, RAID 50 also has some disadvantages. One of the main disadvantages is its complexity. RAID 50 configuration requires a minimum of six drives and two RAID 5 arrays, which makes it more complex to configure and manage. It also requires a higher number of drives, which can increase the cost of the storage system.
RAID 50 is a nested RAID configuration that combines the features of RAID 5 and RAID 0. It provides high fault tolerance and performance, making it suitable for highly available and reliable applications. This RAID level provides a balance between performance and fault tolerance, making it a popular choice for many businesses and individuals.
FAQ - RAID 50 Array
What are the common reasons for RAID 50 failures?
RAID 50 failure can occur due to multiple disk failures, hardware malfunctions, or human error. Minimize risk with a strong backup strategy and regular RAID health checks.
How does RAID 50 handle disk failures?
In a RAID 50 array, a failed disk in any RAID 5 sub-array allows it to function with reduced performance due to distributed parity until replacement. However, if two disks in the same sub-array fail before rebuilding, data is lost.
Are there any disadvantages to RAID 50?
RAID 50 drawbacks are higher costs from needing at least six drives, complex setup, and the risk of data loss if multiple drives in a RAID 5 array fail, highlighting the need for regular backups.
How does RAID 50 compare to RAID 10 in terms of performance and fault tolerance?
RAID 50 balances performance, capacity, and data protection better than RAID 10, offering more storage and similar performance with a tolerance for a single drive failure per RAID 5 array. Yet, RAID 10 may be preferred in environments where disk failure is a major concern due to its simpler rebuilding process.
What type of hardware is required for RAID 50?
RAID 50 needs a controller supporting RAID 5 and 0, with enough power for striping and parity across multiple disks. Use enterprise-grade drives to reduce disk failure risk.