RAID systems are known for their performance, redundancy, and reliability, making them a preferred choice for businesses and IT professionals who depend on continuous data access.
However, despite their robust structure, RAID arrays are not immune to data loss. A single malfunction in one or more drives, power disruptions, or user mistakes can quickly compromise even the most secure setup.
When RAID data loss occurs, it can interrupt operations, corrupt critical databases, or make large volumes of files inaccessible. Understanding why these failures happen is the first step toward preventing them.
If your RAID system has already failed or your data is no longer accessible, contact RAID Recovery Services for expert evaluation and secure recovery assistance.

What RAID Is and Why Data Loss Still Happens
RAID, or Redundant Array of Independent Disks, combines multiple hard drives into a single storage unit to improve performance, capacity, or fault tolerance.
Depending on the RAID level, data can be mirrored, striped, or distributed with parity to protect against drive failure. These configurations help reduce downtime and ensure faster access to stored information.
However, RAID is often misunderstood as a complete safeguard against data loss. While redundancy offers protection from certain drive failures, it does not defend against all risks.
A sudden power surge, multiple simultaneous drive failures, or a corrupted RAID controller can still cause total data loss.
In addition, human errors such as incorrect rebuilds or formatting the wrong disk often result in permanent data loss.
Even though RAID provides strong performance and reliability, it should never replace a dedicated backup strategy. For deeper insights, explore our post on why RAID is not backup.
Common Causes of RAID Data Loss
RAID arrays can fail for many reasons, ranging from hardware issues to accidental human actions. Understanding these causes can help you take preventive steps and respond effectively when problems occur. Below are the most common reasons RAID systems experience data loss:
- Multiple Drive Failures: RAID configurations such as RAID 0 and RAID 5 become highly vulnerable if more than one disk fails. Once redundancy is lost, stored data can no longer be rebuilt.
- Power Surge or Outage: Sudden loss of power or voltage spikes can interrupt write operations, leading to file system corruption and damaged parity information.
- RAID Controller Malfunction: A failed or outdated controller may disrupt data mapping between drives, making the array unreadable.
- Firmware Corruption: Corrupted firmware on one or more drives can prevent them from initializing correctly, resulting in partial or total data loss.
- Accidental Rebuilds or Formatting: Human mistakes, such as selecting the wrong drive during configuration or reinitializing the array, often destroy original data structures.
- Overheating or Physical Damage: Poor ventilation or vibration can cause drive degradation and eventual failure.
When these issues occur, do not attempt to rebuild or reconfigure the array yourself. Instead, seek professional help. Learn more about identifying and troubleshooting RAID failures.
Hardware-Related RAID Failures
Hardware problems are among the most common reasons for RAID data loss. Even though RAID arrays are designed for reliability, the physical components within each drive can still wear out or malfunction over time.
Every hard drive has a limited lifespan. Mechanical parts such as read/write heads or spindle motors may fail after years of operation, leading to unreadable sectors or complete drive failure.
Excessive heat can degrade electronic components and shorten the life of RAID disks. Systems running continuously without proper cooling are especially prone to this issue.
Unstable or insufficient power can damage multiple drives simultaneously. Using a reliable power source or UPS helps minimize the risk of corruption during outages.
Vibration, shock, or improper handling during maintenance can cause irreversible damage to drive platters.
Once any of these issues occur, continuing to operate the array may worsen the damage. Stop using the system immediately and contact professionals who can safely diagnose and recover the data. To learn more, visit our post about RAID hard drive failure.
Software and Configuration Problems
RAID data loss is not always caused by physical damage. Software-related issues and incorrect configurations can also lead to corruption or complete inaccessibility of stored data.
Attempting to rebuild an array without understanding its configuration can result in data being overwritten. Many users unintentionally destroy original parity information during this process.
Corrupt firmware updates or system software errors can prevent drives from syncing properly. Inconsistent metadata between disks often makes the entire RAID unreadable.
If the operating system or file structure becomes damaged, even a healthy RAID setup may fail to mount or display data correctly.
Changes in RAID settings, wrong drive order, or mismatched parameters after replacing a disk can all cause logical inconsistencies.
Outdated or failed RAID controller drivers can interfere with drive communication, disrupting the data flow across the array.
These types of failures require specialized tools and technical knowledge to recover data safely. Learn more about avoiding mistakes during array restoration in our post on RAID rebuild data loss risks.

Preventing RAID Data Loss
Although RAID systems are built for redundancy, preventive measures are essential to protect your data from unexpected failures. Regular monitoring, smart maintenance, and reliable backups can significantly reduce the risk of data loss.
Maintain Regular Backups: Even with redundancy, RAID is not a backup solution. Keep copies of critical data on separate devices or secure cloud storage to ensure accessibility in case of failure.
Monitor Drive Health: Use monitoring tools to check temperature, error rates, and overall disk performance. Replacing a drive before it fails helps maintain array stability.
Use an Uninterruptible Power Supply (UPS): A UPS prevents power surges and sudden outages that can interrupt write operations and damage data integrity.
Avoid DIY Rebuilds: When a RAID fails or becomes degraded, never attempt to rebuild it without understanding the configuration. Incorrect rebuilds can overwrite original data permanently.
Update Firmware and Controllers Carefully: Always verify firmware updates before installation. Back up data beforehand and avoid making multiple system changes at once.
For more detailed guidance, explore our post on data loss prevention.
Fast turnaround times for business-critical data
Professional RAID Recovery Solutions
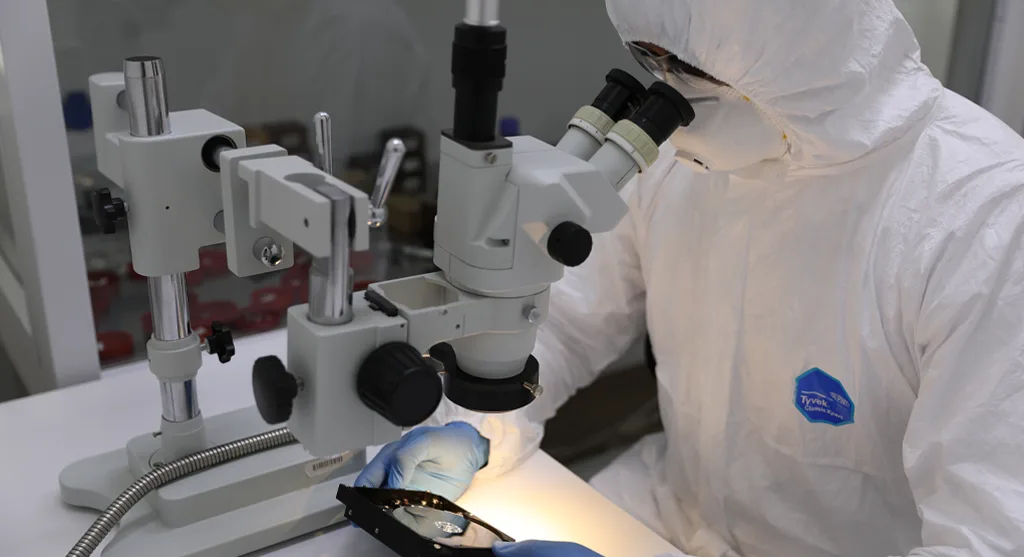
When a RAID system fails, professional recovery is often the safest and most effective solution. Specialists have the tools and expertise to diagnose the problem, rebuild the array, and restore data without causing further damage.
At RAID Recovery Services, our engineers begin with a detailed evaluation to determine the type and extent of failure. Each drive is carefully imaged to preserve its original state before recovery begins. Once the images are secured, the array is reconstructed in a controlled environment to extract data safely.
Our team is equipped to handle a wide range of RAID failures, including drive malfunctions, controller corruption, and logical errors. We work on arrays configured in RAID 0, 1, 5, 6, 10, 50, and more.
Attempting a rebuild or recovery using general software tools can permanently overwrite valuable information. Instead, allow professionals to manage the process.
If your array has stopped working or your files have become inaccessible, contact RAID Recovery Services today to start a secure evaluation and recover your data efficiently.

Conclusion
RAID systems offer a strong balance of speed, capacity, and reliability, but they are not completely immune to data loss. Hardware damage, software corruption, or incorrect rebuild attempts can all lead to serious data inaccessibility. By understanding the main causes and following preventive steps, you can minimize the risks and ensure your critical data remains secure.
If your RAID array has failed or you suspect corruption, do not attempt to fix it on your own. Contact RAID Recovery Services to speak with experienced engineers who can evaluate your system and restore your data with precision and care.
Trust the experts with proven results
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the most common causes of RAID data loss?
RAID data loss often occurs due to multiple drive failures, power surges, controller malfunction, or incorrect rebuilds. Software corruption, firmware damage, and human errors during maintenance can also lead to serious data loss incidents.
Can RAID prevent all types of data loss?
No. RAID provides redundancy but not full protection. It safeguards against some drive failures but cannot prevent data loss caused by user mistakes, file corruption, or natural disasters. Keeping regular backups is essential for complete data protection.
What should I do if my RAID system fails?
Stop using the array immediately to avoid further damage. Do not rebuild or reinitialize the RAID. Instead, contact professional specialists who can diagnose the issue and perform recovery in a secure environment.
Can I recover lost RAID data using software?
DIY software can worsen the situation by overwriting data or damaging array structures. Professional recovery services use specialized tools to safely extract data without risking permanent loss.
How does RAID Recovery Services handle RAID data loss cases?
Our engineers perform a full diagnostic evaluation to identify the cause of failure. Each drive is imaged individually before rebuilding the array in a controlled lab environment. This ensures maximum recovery success with minimal risk.