A NAS (Network Attached Storage) is a device that connects to a network and provides shared storage space for multiple users. It can be used for various purposes, such as backup, file sharing, media streaming, and more.
RAID (Redundant Array of Inexpensive Disks) is a technology that combines multiple disks into a single logical unit to improve data redundancy, performance, or both. In this blog post, we will discuss the different RAID levels and which one to choose for a NAS.
RAID 0 for NAS
RAID 0 is the simplest RAID level that strips data across two or more disks without redundancy. This means that if one disk fails, all data is lost. However, RAID 0 provides the best performance among all RAID levels because it can read and write data from/to multiple disks simultaneously.
Therefore, it is a good choice for applications that require high-speed data transfer, such as video editing, gaming, and scientific computing. However, RAID 0 is not recommended for important or irreplaceable data.
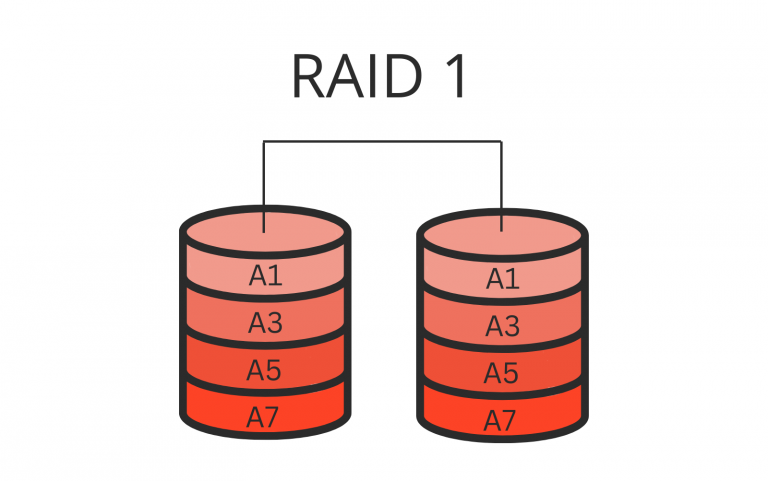
RAID 1 for NAS
RAID 1, known as a mirroring RAID level, operates by duplicating data across two or more disks, ensuring an exact copy of all information is maintained on each disk. This redundancy means that should one disk encounter failure, the remaining disk(s) still possess a complete copy of all the data, thus preventing data loss.
Consequently, RAID 1 is recognized for offering the highest level of data redundancy among all RAID configurations. This halves storage capacity as data is duplicated across disks.
RAID 1 has lower storage efficiency. However, it is preferred for applications that prioritize data availability over capacity or write speed.
It’s perfect for email servers that demand continuous data access. It suits databases that need steadfast data integrity and financial systems where data accuracy and availability are paramount. In these cases, the importance of uninterrupted data access far surpasses worries about storage space. The slower write speeds associated with data mirroring in RAID 1 become a secondary concern.
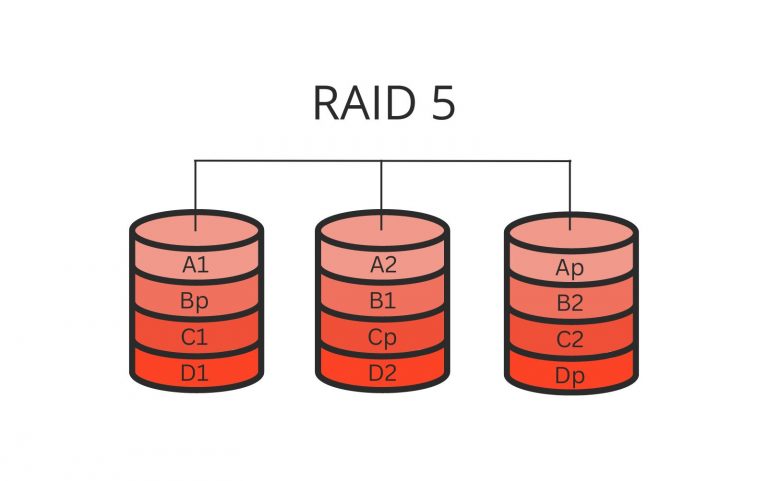
RAID 5 for NAS
Characterized by its unique approach, a parity RAID level utilizes three or more disks to distribute data, with one disk exclusively dedicated to parity. This mathematical function ensures data integrity, enabling data reconstruction in the event of a disk failure.
This approach boosts system resilience against disk failures by using parity information and data from remaining disks for reconstruction. In the event of a disk failure, the lost data can be recreated, maintaining system integrity.
This mechanism enhances data security and ensures system resilience. RAID 5 is an ideal choice for environments prioritizing data availability and security.
RAID 5 provides good data redundancy and performance, but it also has some drawbacks. Firstly, it requires at least three disks, reducing the storage capacity by one disk. Secondly, RAID 5 has a write penalty, meaning every write operation requires multiple disk accesses. Therefore, RAID 5 is a good choice for applications requiring data redundancy and performance, such as file servers, web servers, and virtualization hosts.
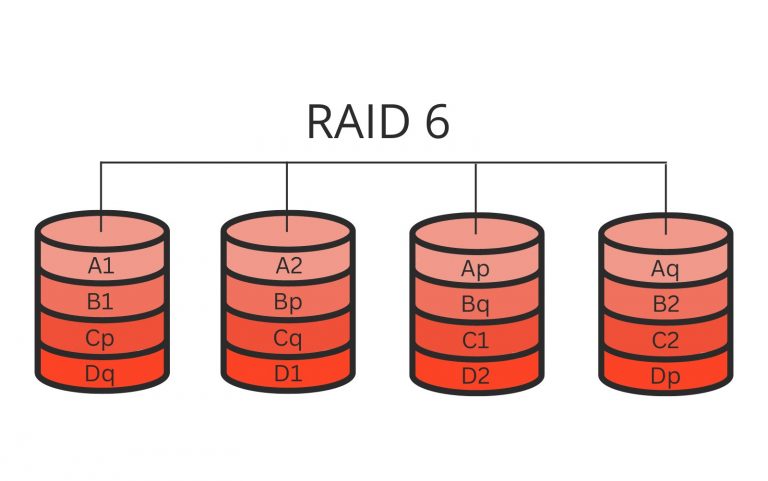
RAID 6 for NAS
RAID 6 builds on RAID 5, offering better data protection with two disks for parity, not just one. RAID 6 employs a dual parity system, enhancing data security. It withstands two disk failures without data loss. This capability makes RAID 6 a more reliable option for systems where data integrity is paramount.
While RAID 6 offers better data redundancy and reliability than RAID 5, it requires extra disks, reducing the available storage capacity by two disks.
RAID 6 offers enhanced data protection by sacrificing some potential storage space. This trade-off is crucial for organizations prioritizing high data security and redundancy.
Moreover, RAID 6 has a higher write penalty than RAID 5 because it needs to calculate two parity blocks for every write operation. Therefore, RAID 6 is a good choice for applications that require high data redundancy and can tolerate the performance overhead, such as large file servers, media storage, and backup systems.
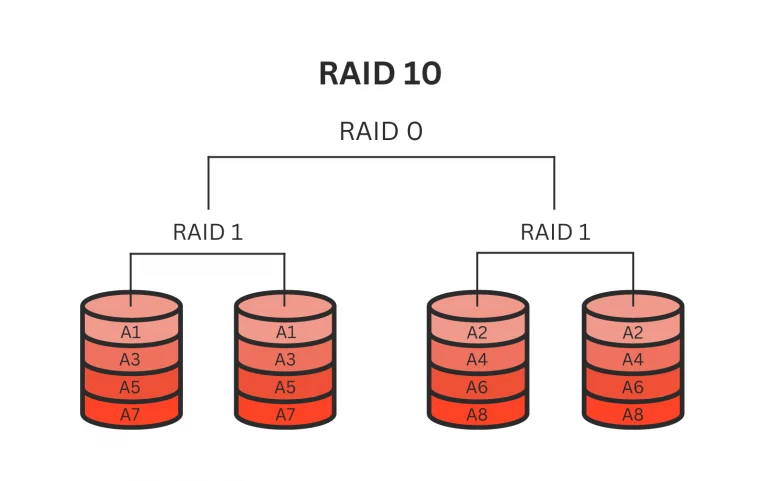
RAID 10 for NAS
RAID 10, a hybrid of RAID 1 and RAID 0, mirrors data across two or more disk pairs and then stripes across those pairs. This unique setup offers the dual benefits of robust data redundancy and enhanced performance. To implement RAID 10, a minimum of four disks is required, effectively halving the total storage capacity due to the mirroring process.
Despite its higher cost per usable gigabyte due to requiring twice as many disks as other RAID configurations, RAID 10’s architecture delivers superior fault tolerance and read/write speeds.
This makes it ideal for applications where data integrity and performance are critical, like high-transaction database systems or environments prioritizing speed and data protection.
Therefore, RAID 10 is a good choice for applications requiring high data redundancy and performance, such as database servers, virtualization hosts, and mission-critical systems.
How to Choose the Best RAID for NAS
Selecting a NAS RAID level depends on disk count, capacity, redundancy, performance, and budget. Here are some guidelines to help you choose the right NAS RAID types:
- If you have only two disks and need maximum performance, choose RAID 0. However, be aware that you will lose all data if one disk fails.
- If you have only two disks and need data redundancy, choose RAID 1. However, be aware that you will lose half of the available storage capacity.
- If you have three or more disks and need a balance between data redundancy and performance, choose RAID 5. However, be aware that RAID 5 has a write penalty and requires at least three disks.
- If you have five or more disks and need higher data redundancy, choose RAID 6. However, be aware that RAID 6 has a higher write penalty and requires more disks.
- If you have four or more disks and need both high data redundancy and performance, choose RAID 10. However, be aware that RAID 10 requires twice as many disks as other RAID levels.

In choosing the right RAID level, consider other factors too. These include disk quality, cooling, power supply, and network connectivity. Regularly monitor your NAS’s health and status. Perform backups to protect data against failures and errors. RAID technology enhances your NAS’s reliability and performance.
The right RAID level depends on disk number, storage capacity, redundancy, performance, and budget. Follow the guidelines and best practices in this post for an informed decision. Build a NAS that meets your expectations.
Frequently Asked Questions
Should I consider a RAID configuration if I only have one disk in my NAS?
If your NAS only has one disk, RAID configurations are not possible since RAID involves managing data across multiple disks. To prevent data loss, it is recommended that you back up important data to cloud storage or an external drive.
What happens if a disk fails in a RAID 5 or RAID 6 setup?
In RAID 5 or 6 setups, if a disk fails, the system still runs by using parity data to instantly rebuild the lost information. You should replace the failed disk as soon as possible to restore full redundancy and ensure the array can survive another disk failure.
How often should I check the health of my NAS RAID array?
It’s advisable to monitor the health of your NAS RAID array regularly, at least once a month. Most NAS systems provide built-in tools for checking disk health and the status of the RAID array, alerting you to potential issues before they result in data loss.
Can I change the RAID level of my NAS after setting it up?
Many NAS systems allow RAID changes post-setup, but it’s slow and usually requires data backup. Some advanced models offer RAID migration without data loss but always back up data to avoid loss.
Do I need specialized software to manage my NAS RAID configuration?
Most NAS devices have built-in software for managing RAID configurations. Third-party RAID tools exist but are often unnecessary for home and small office users.
Is RAID a substitute for regular backups?
No, RAID can’t replace regular backups. RAID setups guard against hardware failure but not against data loss from software problems, cyber-attacks, or accidental deletion. Regular backups to separate devices or cloud storage are essential for comprehensive data protection.